Metastatic disease to the liver: 11% (86 votes)
Cirrhosis likely secondary to ethanol:28% (213 votes)
Cirrhosis likely secondary to Hepatitis C:33% (253 votes)
Multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma:28% (212 votes)
Discussion
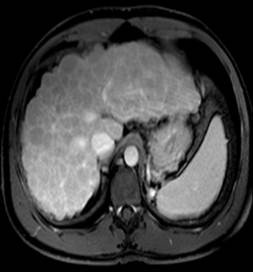
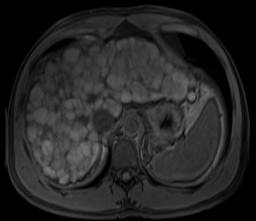
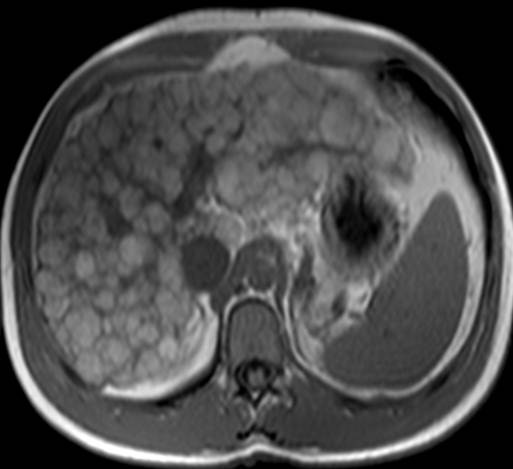
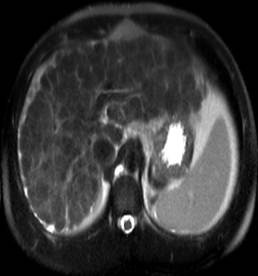
This is a great example of macronodular cirrhosis. The most common cause of cirrhosis, chronic ethanol consumption, is micronodular cirrhosis. Hepatitis C, an increasingly common cause of cirrhosis in the United States, is a cause of macronodular cirrhosis and was the etiology of the cirrhosis in this case. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma is important in this population.
The classic morphologic changes of cirrhosis are demonstrated in this case. There is enlargement of the caudate and lateral segment of the left lobe of the liver with atrophy of the right lobe and medial segment of the left lobe. There is a markedly nodular liver contour.
References
Gupta AA, Kim DC, Krinsky GA, et al. CT and MRI of cirrhosis and its mimics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:1595-1601.
Zhang BH, Yang BH, Tang ZY. Randomized controlled trial of screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:417-422.
|

|