定义:肺栓塞(pulmonary embolism,lung embolism)是内源性或外源性栓子阻塞肺动脉或其分支引起的肺循环障碍。 Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of the main artery of the lung or one of its branches by a substance that has travelled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream。 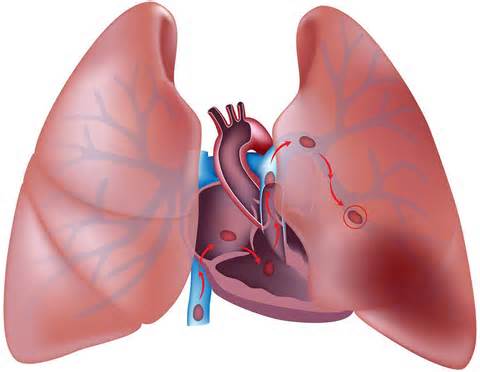 国际疾病分类 ICD-10 126 国际疾病分类 ICD-9 425.1 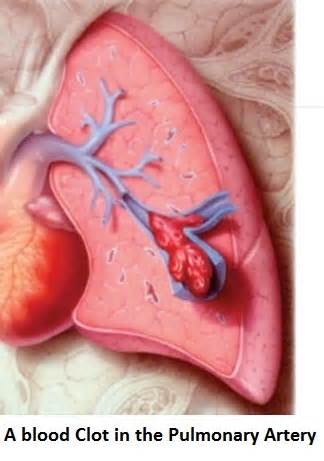 定义: Pulmonary embolism: Sudden closure of a pulmonary artery or one of its branches, caused by a blood-borne clot or foreign material that plugs the vessel.
Pulmonary Embolism: "The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung."
PE refers to obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by material (eg, thrombus, tumor, air, or fat) that originated elsewhere in the body. PE can be classified as acute or chronic. Patients with acute PE typically develop symptoms and signs immediately after obstruction of pulmonary vessels. In contrast, patients with chronic PE tend to develop slowly progressive dyspnea over a period of years due to pulmonary hypertension 急性肺栓塞(Acute pulmonary embolism,PE)是常见和致命性疾病,其死亡率可以通过迅速的诊断和治疗。不幸的是,PT的临床表现是多种多样的,没有特医生,是精确地诊断成为困难的事。 肺栓塞自然病史- 肺栓塞不治疗死亡率接近30%【1-4】。反复发生的肺栓塞是最常见的死亡原因。未治疗的存活者并发症是不知的,但似乎是很高的。 本栏目将复习急性PE的发病率,自然病史,病理生理,危险因素,症状体征以及结果。 1. Horlander KT, Mannino DM, Leeper KV. Pulmonary embolism mortality in the United States, 1979-1998: an analysis using multiple-cause mortality data. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163:1711. |

|